Research
Precise motion control is desired in a variety of industrial robot applications. In order to achieve precise and rapid rest-to-rest motion, the overshoot and the residual vibration caused by flexibility of robots should be minimized. To make robot motion more accurate, vibration suppression and control of flexible joint robot problems are introduced in this research. Furthermore, considering these control problems can be addressed using more general optimal control approach, an efficient numerical method for optimal control is presented not only to dress motion control problems, but also other applications like motion planning.
Vibration Suppression
This work try to suppress vibration for robot with flexible payload. A modified input shaping technique, which is designed to work without slowing the motion, is implemented in this work. Acceleration at the end tip of payload shows the performance of the vibration suppression.
Related publications
Zhao, Yu, and Masayoshi Tomizuka. “Modified Zero Time Delay Input Shaping for Industrial Robot With Flexibility.” In ASME 2017 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, pp. V003T22A003-V003T22A003. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2017. [DOI]
Zhao, Yu, Wenjie Chen, Te Tang, and Masayoshi Tomizuka. “Zero time delay input shaping for smooth settling of industrial robots.” In Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 2016 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 620-625. IEEE, 2016. [DOI]
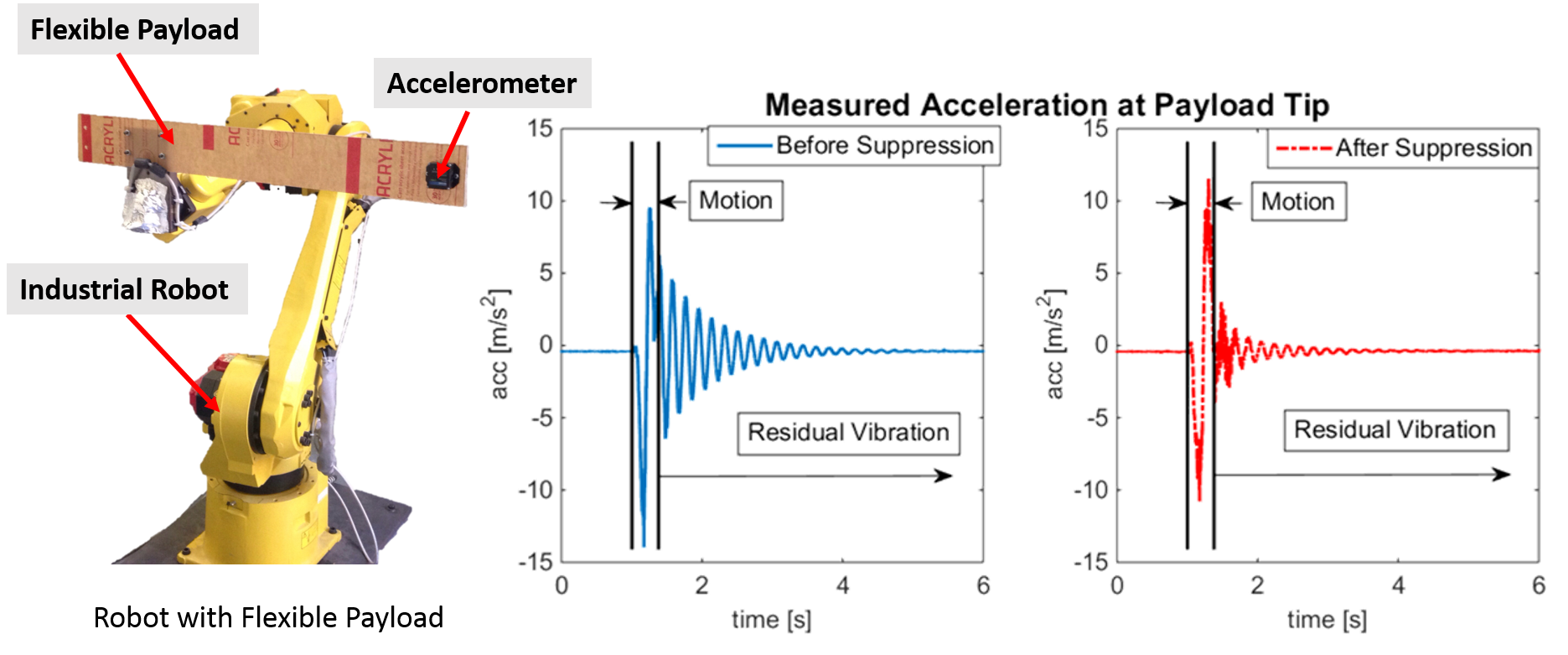 |
Efficient Numerical Method for Optimal Control
A variety of control problems can be formulated and solved as optimal control problem. However, it is difficult to implement numerical control in practice due to two reasons. One reason is that no simple analytical solution exists for general nonlinear optimal control problems. Another reason is that the computational load for numerical solution is typically heavy. In this work, efficient numerical method is developed for general nonlinear optimal control problems. Potential applications of this work include control of underactuated systems, trajectory and motion planning of robot manipulators, and so on.
Related publications
Zhao, Yu, Hsien-Chung Lin, and Masayoshi Tomizuka. “Efficient trajectory optimization for robot motion planning.” In International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), 2018. [preprint version]
Lin, Chung-Yen, Yu Zhao, Masayoshi Tomizuka, and Wenjie Chen. “Path-constrained trajectory planning for robot service life optimization.” In American Control Conference (ACC), 2016, pp. 2116-2122. IEEE, 2016. [DOI]
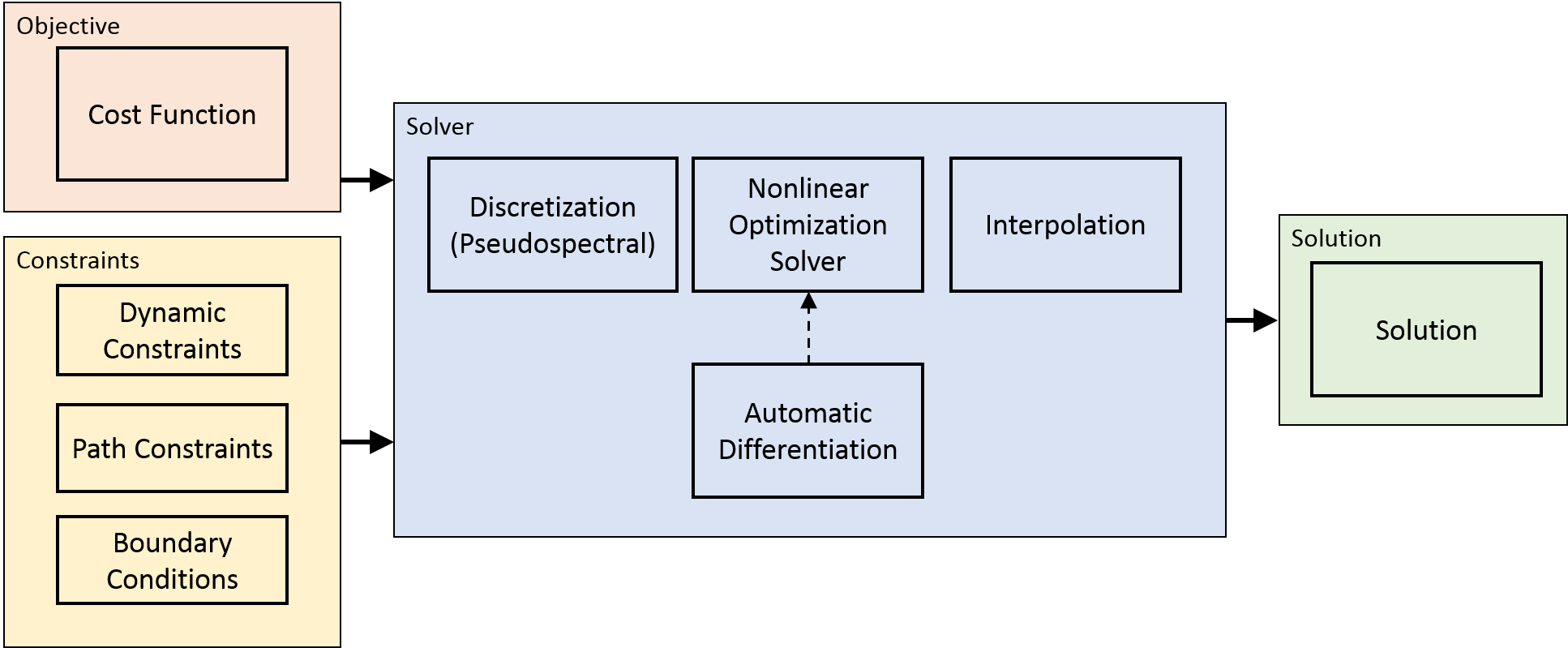 |
Example: Time optimal motion Planning of 6 Joint Robot with kinematics, dynamics constraints, and collision avoidance requirements.
Example: Quadrotor Flipping [link to code] and Motion Planning of 2 Link Planar Robot
Example: Time optimal motion Planning of 6 Joint Robot, using CppAD and CasADi respectively
Motion Control of Flexible Joint Robot
This work try to improve trajectory tracking accuracy of flexible joint robot. A MATLAB/SimMechanics simulator for 6-joint robot is developed. Joint flexibility effect is also considered in this simulator that simulates robot dynamics. For very soft joint, the solution is implementing a multiple sliding surface controller (MSSC) that takes advantage of the model of robot dynamics and sensing from actuator and robot joints/links.
Related publications
Zhao, Yu, Xiaowen Yu, and Masayoshi Tomizuka. “Neuroadaptive Control for Trajectory Tracking of Indirect Drive Robots.” In ASME 2017 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, pp. V002T12A004-V002T12A004. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2017. [DOI]
Zhao, Yu, Cong Wang, Xiaowen Yu, and Masayoshi Tomizuka. “Complete Dynamic Modelling of Flexible Joint Robots.” In ASME 2015 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, pp. V001T18A003-V001T18A003. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2015. [DOI]